Gross Profit vs. Net Profit: Formula, Analysis & Examples
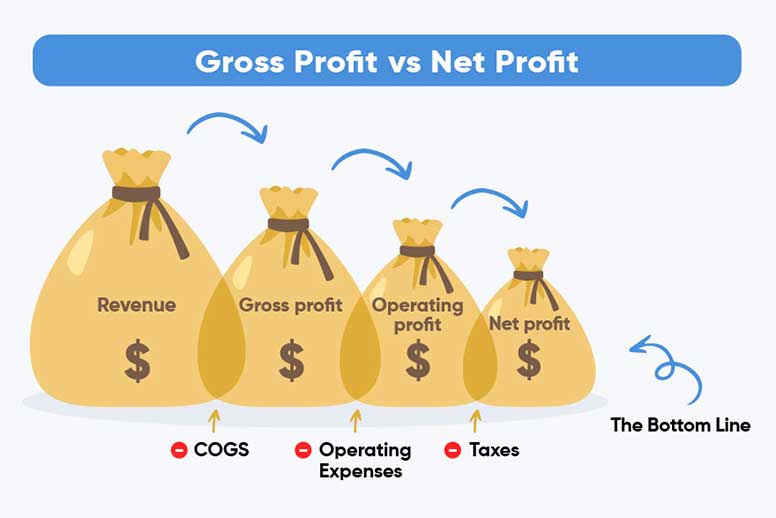
Gross Profit is a financial metric that represents a company’s revenue after deducting the cost of goods sold (COGS). It is a critical measure of profitability, indicating how efficiently a business produces and sells its products or services.
What is Gross Profit?
Gross Profit
Also known as Revenue, it is calculated by subtracting direct costs like materials, labor, and manufacturing from total revenue. This figure highlights the business’s ability to cover its production costs and still generate a profit.
A higher gross profit margin suggests a company is managing production costs well, while a lower margin may indicate inefficiencies.
This business metric plays a vital role in understanding business performance, and guiding decisions on pricing, budgeting, and overall financial health.
Table of Contents
What is Net Profit?
Net Profit
Total earnings a business retains after deducting all expenses, such as COGS, Operating Costs, Interests, and Taxes, from its Gross Profit or Revenue.
For contractors like plumbers, landscapers, cleaners, HVAC professionals, and small business owners, net profit represents the true financial health of their business, showing how much money they keep after covering labor, materials, overhead, operating costs, interests, taxes, and other costs.
Maximizing net profit helps contractors and any kind of business owner, sustain and grow their operations while ensuring long-term success.

How to calculate Gross and Net Profit?
To calculate Gross Profit, use the following formula:
Gross Profit = Revenue – Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
Where:
- Revenue is the total income from sales.
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) includes the direct costs of producing the goods or services sold, such as materials and labor.
To calculate Net Profit, use the following formula:
Net Profit = Revenue – (COGS + Operating Expenses + Interests + Taxes)
Where:
- Revenue is the total income from sales.
- COGS is the Cost of Goods Sold.
- Operating Expenses include costs like rent, utilities, and salaries.
- Interest refers to any interest payments on loans.
- Taxes include any income or business taxes owed.

Try our Profit Margin calculator
Do you need help calculating your Gross and Net Profit Margin? Try our Profit Margin Calculator for free.
What does Gross Profit tell you?
It shows how efficiently a business is generating profit from its core operations, specifically the production and sale of goods or services.
It measures the difference between Revenue and the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS), highlighting the ability to manage production costs while maintaining sales.
1. Operational Efficency
A higher gross profit means the business is effectively controlling production or service costs relative to its sales.
2. Profitability Before Expenses
It shows profitability before accounting for indirect expenses like administrative, marketing, taxes, and interest.
3. Pricing and Cost Strategy
Gross profit helps evaluate if a business’s pricing strategy and production costs are aligned to maintain profitability.
What does Net Profit tell you?
Net Profit provides a comprehensive measure of a business’s overall profitability after accounting for all expenses, including operating costs, taxes, interest, and any other deductions.
It represents the actual financial gain or loss over a given period and is a key indicator of a company’s financial health.
1. True Profitability
Net profit shows how much money remains after all business expenses, giving a clear picture of the company’s actual earnings.
2. Financial Sustainability
It helps assess whether the business is financially sustainable in the long term by indicating if revenues exceed total costs.
3. Business Efficiency
By highlighting the bottom line, it reflects how efficiently a business manages all aspects of its operations, from production to overhead costs.

What is a good Gross Profit Margin?
It generally depends on the industry, but for most businesses, a margin of between 20% to 40% is considered healthy.
For contractors, like plumbers, carpenters, HVAC specialists, and landscapers, tends to fall within the 30% to 50% range.
This margin allows businesses to cover operating costs, reinvest in growth, and ensure profitability after all expenses are accounted for.
A higher number indicates greater efficiency in managing direct costs, such as labor and materials, allowing for more flexibility in pricing and long-term financial health.
What is a good Net Profit Margin?
A good Net Profit Margin typically varies by industry, but a general benchmark for most businesses is around 10% to 20%. For contractors, such as plumbers, electricians, HVAC specialists, and landscapers, a net profit margin of 5% to 15% is considered healthy.
Achieving a higher net profit margin indicates that a business effectively controls its overall costs and expenses relative to its revenue.
A net profit margin above 15% is particularly impressive and suggests strong financial health, enabling businesses to reinvest in operations, manage economic fluctuations, and provide returns to stakeholders.
Ultimately, the ideal net profit margin will depend on factors like market conditions, competition, and specific operational costs within the contracting industry.
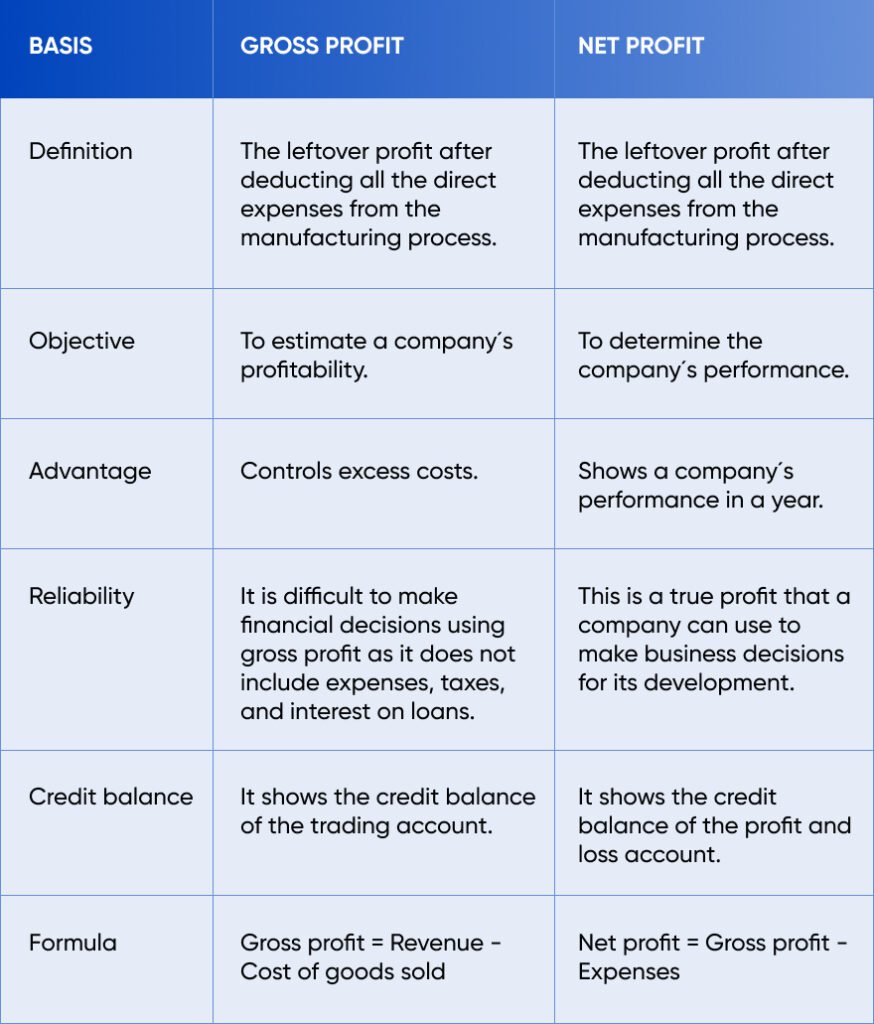
Comparison Chart
Plumbing Business Example
Here’s a simple example illustrating how a small plumbing business can calculate its revenue for 2024 using gross profit margin and net profit margin.
Example: Plumbing Small Business Financial Calculation
Assumptions:
1. Projected Revenue for 2024: $200,000
2. Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): $80,000
3. Total Operating Expenses (including salaries, rent, utilities, etc.): $70,000
4. Interest and Taxes: $10,000
Step 1: Calculate Gross Profit
Formula:
Gross Profit = Revenue – Cost Of all Goods Sold (COGS)
Calculation:
Gross Profit = $200.000 – $80.000 = $120.000
Step 2: Calculate Gross Profit Margin
Formula:
Gross Profit Margin = (Gross Profit / Revenue) x 100
Calculation:
Gross Profit Margin = ($120.000 / $200.000) x 100 = 60%
Step 3: Calculate Net Profit
Formula:
Net Profit = (Revenue – COGS – Operating Expenses – Interests – Taxes)
Calculation:
Net Profit = ($200.000 – $80.000 – $70.000 – $10.000) = $40.000
Step 4: Calculate Net Profit Margin
Formula:
Net Profit Margin = (Net Profit / Revenue) x 100
Calculation:
Net Profit Margin = ($40.000 / $200.000) x 100 = 20%
In this example, the plumbing small business is projected to generate a revenue of $200,000 in 2024, achieving a gross profit margin of 60% and a net profit margin of 20%.
This indicates that while the business is efficiently managing its direct costs, it also has a healthy bottom line after accounting for all operating expenses, interest, and taxes.

Roger is a Digital Marketeer passioned about SaaS & Mobile App products.
He considers himself a geek about invoicing, accounting, and related topics. He loves helping out contractors, freelancers, and small business owners achieve their goals when running their businesses.
